ABSTRACT
The results of measurements of heat conduction (К), heat capacity (CP), electrical resistance (r) and data of differentially scanning calorimetry (DSC) of
Ni50.2Mn39.8In10 Geissler alloy in Т=25 – 350 К interval are given. The anomalies evidencing on the phase transitions of I and II orders
with TC=321 К, MS=296 К are observed on curves of DSC and CP(T). The strong increase of heat conduction at transition martensite – austenite
ΔK=3.2 Vt/m*К caused by the increase of electron contribution because of the electron mobility increase at transition in high-symmetry phase, is revealed.
The lattice heat conduction changes insignificantly at the transition that shows on the insensibility of phonons to structural disorder.
Keywords: Geissler alloys, heat conduction, heat capacity, phase transitions, electrical resistance.
DOI:10.70784/azip.3.2024CE27
Received: 2024
Internet publishing: 2024
AUTHORS & AFFILIATIONS
* Institute of Physics named after Kh.I. Amirkhanov, DFIC RAS, Makhachkala, Russia
**Institute of radio engineering and electronics named after V.A.Kotelnikov, ДФИЦ RAS, Moscow, Russia
e-mail: ab.batdalov@gmail.com, e-mail: hanov82@mail.ru
e-mail: mukhuch87@mail.ru, e-mail: a.v.mashirov@mail.ru, e-mail: lowtemp@mail.ru
Graphics and Images
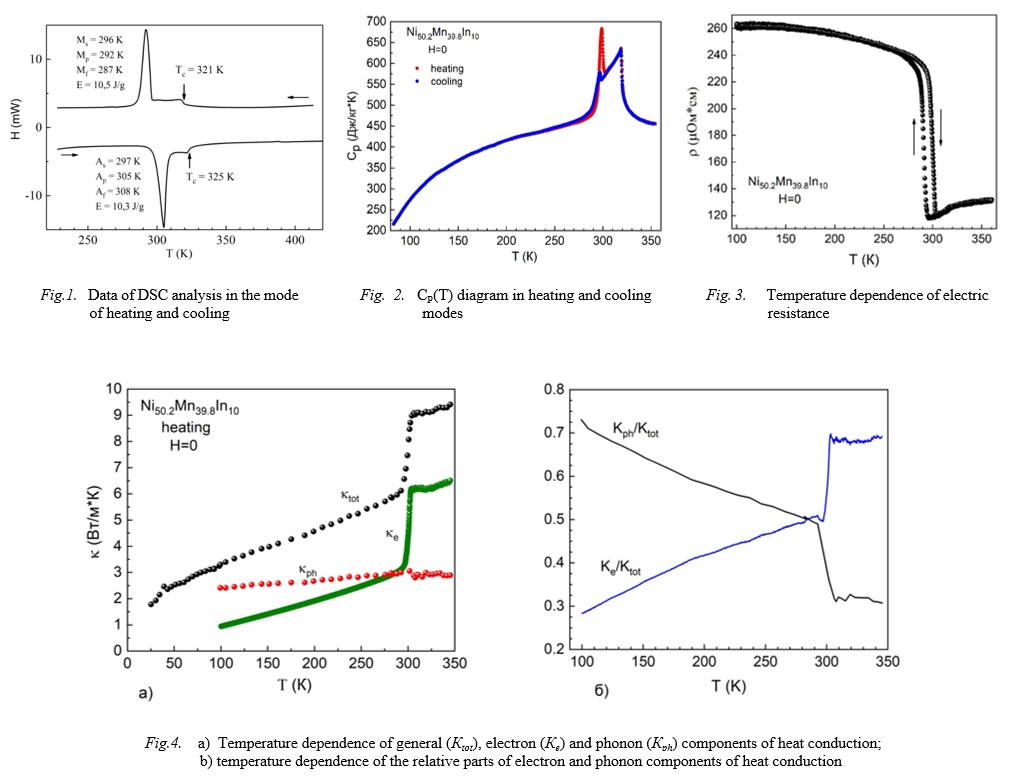
Fig.1-2-3-4
|
[1] V.D. Buchelnikov, S.V. Taskayev, M.A. Zagrebin, P. Etel. JETP letters 85, 689 (2007).
[2] V.V. Khovaylo, T. Kanomata, T. Tanaka, M. Nakashima, Y. Amako, R. Kainuma, R.Y. Umetsu, H. Morito, and H. Miki. Phys. Rev. B 80, 144409 (2009).
[3] A.N. Vasilyev, V.D. Buchelnikov, T. Takagi, V.V. Khovaylo, E.I. Estrin. SPS 173, 578 (2003).
[4] L.S.S. Chandra, M.K. Chattopadhyay, V.K. Sharma, S.B. Roy, S.K. Pandey. Phys. Rev. B 81, 195105 (2010).
[5] A.G. Gamzatov, A.B. Batdalov, Sh.K. Khizriyev. Solid state physics 64, 2094 (2022).
[6] A.G. Gamzatov, A.B. Batdalov, A.M. Aliev, Sh.K. Khizriev, V.V. Khovaylo, A. Ghotbi Varzaneh, P. Kameli, I. Abdolhosseini, Sarsari, S. Jannati. Intermetallics 143, 107491 (2022).
[7] J. Kaˇstil, J. Kamar´ad, M. M´ıˇsek, J. Hejtm´anek, Z. Arnold. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 466, 260 (2018).
[8] A.B. Batdalov, A.M. Aliev, L.N. Khanov, V.D. Buchel‘nikov, V.V. Sokolovskii, V.V. Koledov, V.G. Shavrov, A.V. Mashirov, E.T. Dil‘mieva. JETP 122, 874 (2016).
[9] Q. Zheng, G. Zhu, Z. Diao, D. Banerjee and D.G. Cahill. Adv. Eng. Mater. 1801342 (2019).
[10] Y.K. Kuo, K.M. Sivakumar, H.C. Chen, J.H. Su, C.S. Sue. Phys. Rev. B 72, 054116 (2005).
[11] Y.V. Kaletina, E.G. Gerasimov. Solid state physics 56, 1583 (2014).
[12] V.N. Prudnikov, A.P. Kazakov, I.S. Titov, Y.N. Kovarski, N.S. Perov, A.B. Granovskii, I. Dubenko, A. Pathak, N. Ali, J. Gonzales. SSP 53, 460 (2011). [13] A.K. Pathak, B.R. Gautam, I. Dubenko, M. Khan, Sh. Stadler and N. Ali. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 07F315 (2008).
[14] S.M. Podgornykh, E.G. Gerasimov, N.V. Mushnikov, T. Kanomata. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 266, 012004 (2011).
[15] J.L. Cohn, J.J. Neumeier, C.P. Popoviciu, K.J. McClellan, Th. Leventouri. Phys. Rev. B 56, R8495 (1997).
[16] R. Berman. The heat conduction of solid states. World, Moscow. 296 с. (1979).
[17] S. Fujieda, Y. Hasegawa, A. Fujita and K. Fukamuchi. Journal of Applied Physics 95, 2429 (2004).
[18] A. Ghotbi Varzaneh, P. Kameli, V.R. Zahedi, F. Karimzadeh and H. Salamati. Met. Mater. Int. 21, 758-764 (2015).
|
