ABSTRACT
It is know, radiation detection requires high resistance and good charge carrier conductivity. To this end, deep centers, which are effective carrier traps, should be
avoided by using shallow donors and acceptors to compensate carriers. Our calculations allow us to investigate how point vacancies affect the localization of the Fermi
level in the semiconductor band gap. With the increase in the value of the Fermi level, the formation energy of the Cd vacancy approaches from the +2 charge state to the -2
charge state and changes to the -2 charge state at values above the Fermi level of 1.2 eV. This state remains stable in the subsequent increase in the value of the Fermi
level. The calculation shows that the Ga vacancy is stable at -2 charge regardless of the value of the Fermi level, and no charged transition level is observed within the
bandgap. The +2 state in the dot Se vacancy is stable for the Fermi level below 0.5 eV. In the range of 0.5 eV-1.1 eV, the neutral charge state is more stable. Values above
1.1eV and -2 charge states are stable and remain stable regardless of the further increase of the Fermi level.
Keywords: chalcopyrite, defect, formation energy, semiconductor, superlattice
DOI:10.70784/azip.2.2024239
Received: 27.06.2024
Internet publishing: 02.07.2024
AUTHORS & AFFILIATIONS
1. Institute of Physics Ministry of Science and Education Republic of Azerbaijan, 131 H.Javid ave, Baku, AZ-1143, Azerbaijan
2. Azerbaijan State Oil and Industry University, Baku, AZ 1010, Azerbaijan
E-mail: mustafabeyliafet18@gmail.com
Graphics and Images
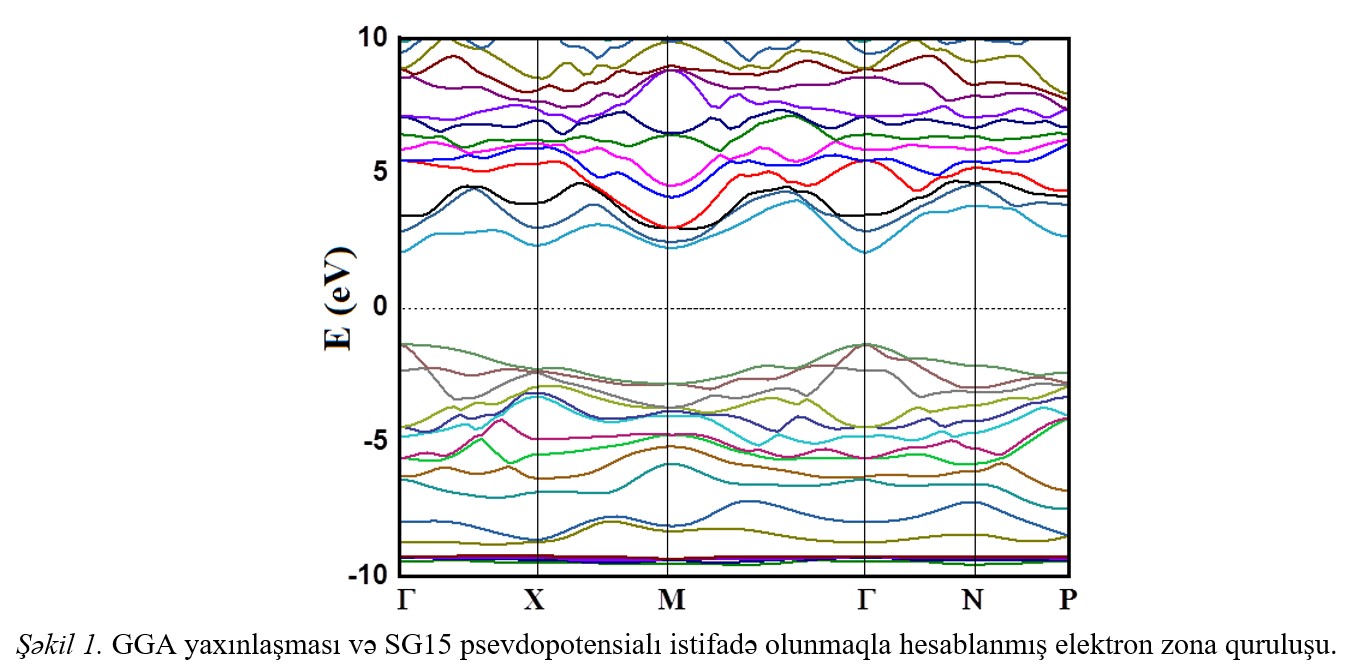
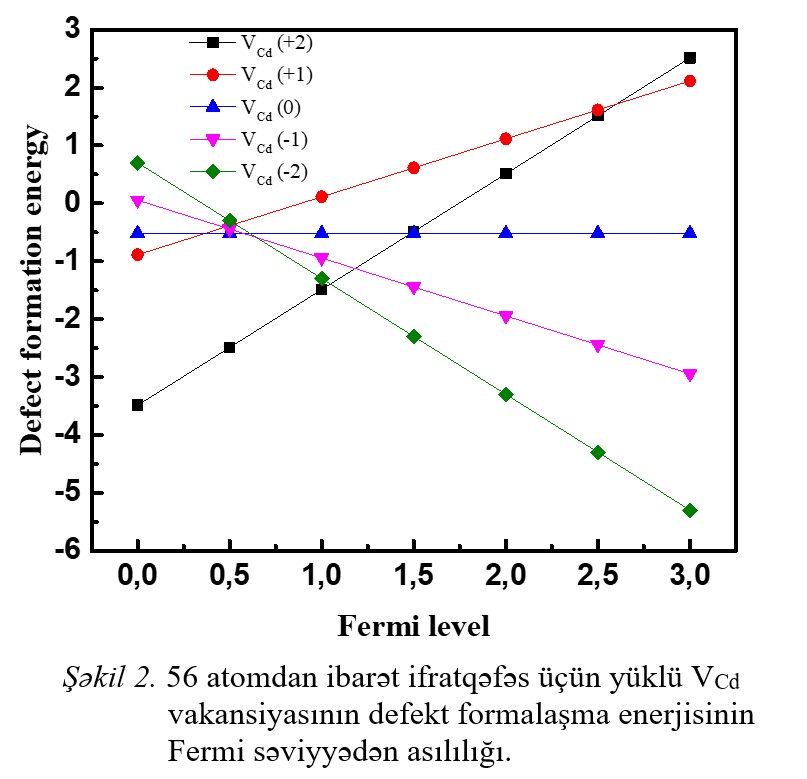
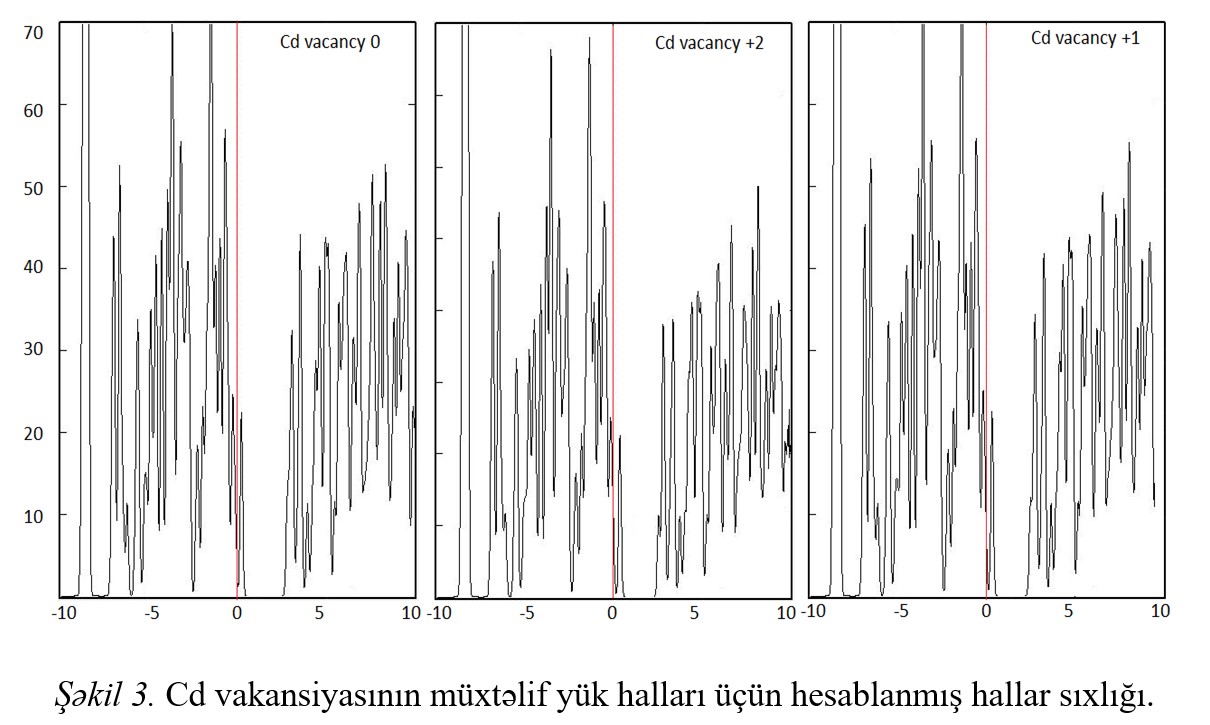
Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3
|
REFERENCIES
[1] S.H. Jabarov, Y.I. Aliyev, T.M. Ilyasli, A.A.Baylarova,A.O. Dashdemirov, V.I. Nasirov, N.A. Ismayilova, G.M. Aghamirzayeva, M.N. Mirzayev. Integrated Ferroelectrics, 221, pp.180-185, 2021.
[2] S.G.Asadullayeva,N.A.Ismayilova,Q.Y.Eyyubov Solid State Communications, 356, pp.114950, 2022.
[3] A.O. Dashdemirov, S.G. Asadullayeva, A.S.Alekperov, N.A. Ismayilova, S.H. Jabarov. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 35, 30, pp.2150305, 2021.
[4] N.A. Ismayilova. Advanced Physical Research, 4, 1, pp.56-59, 2022.
[5] Y.I. Aliyev, N.A. Ismayilova, R.F. Novruzov, A.O. Dashdamirov, H.J. Huseynov, S.H. Jabarov, A.A. Ayubov. Modern Physics Letters B, 33, 21, pp.1950242, 2019.
[6] N.A. Ismayilova, S.H. Jabarov. Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials-Rapid Communications, 11, 5-6, pp.353-356, 2017.
[7] S.H. Jabarov, N.A. Ismayilova, D.P. Kozlenko, T.G. Mammadov, N.T. Mamedov, H.S. Orudzhev, S.E. Kichanov, F.A. Mikailzade, E.K. Kasumova, N.T. Dang. Solid State Sciences, 111, pp.106343, 2021.
[8] N.T. Mamedov, S.H. Jabarov, D.P. Kozlenko, N.A. Ismayilova, M.Yu. Seyidov, T.G. Mammadov, N.T. Dang. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 33, 15, pp.1950149, 2019.
[9] Y.I. Aliyev, P.R. Khalilzade, Y.G. Asadov, T.M. Ilyasli, F.M. Mammadov, N.A. Ismayilova, M.N. Mirzayev, S.H. Jabarov, N.T. Dang. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 33, 28, pp.1950339, 2019.
[10] N.A. Ismayilova, H.S. Orudjev, S.H. Jabarov Semiconductors, 51, 4, pp.473-476, 2017.
[11] O. Madelung. Semiconductors: Data Handbook, 3rd ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2004).
|
