ABSTRACT
The study of thermal and dielectric properties of polymer nanocomposite materials allows us to evaluate the quality of the material and prepare recommendations for
optimizing the technology of its acquisition and production. This work is devoted to the study of various thermal and dielectric properties of the PP+MnO2
nanocomposite based on PP. The thermal-oxidative stability of the obtained nanocomposites is established. It is established that the introduction of various concentrations
of the MnO2 nanoadditive into the polymer and the effect of the ETP field lead to thermal destruction of the polymer and a decrease in its thermal stability. When
polypropylene is exposed to a field E=7*106V/m ETP, partial amorphization of the polymer matrix crystals and thermal stability occur. It is also established that
a change in the permittivity (ε), the dielectric loss tangent (tgδ) is associated with a change in the supramolecular structure of the boundary layers of the polymer matrix
and the interphase interaction between the components of the PP+MnO2 nanocomposite depending on the polarization conditions.
Keywords: electrothermopolarization, thermooxidative destruction, nanoaddition, crystallization, derivatography, depolarization.
DOI:10.70784/azip.2.2024332
Received: 23.09.2024
Internet publishing: 27.09.2024
AUTHORS & AFFILIATIONS
1. Institute of Physics Ministry of Science and Education Republic of Azerbaijan, 131 H.Javid ave, Baku, AZ-1143
2. Baku State University, 23, Z. Khalilov st., Baku, AZ 1148
E-mail: aem05@rambler.ru
Graphics and Images
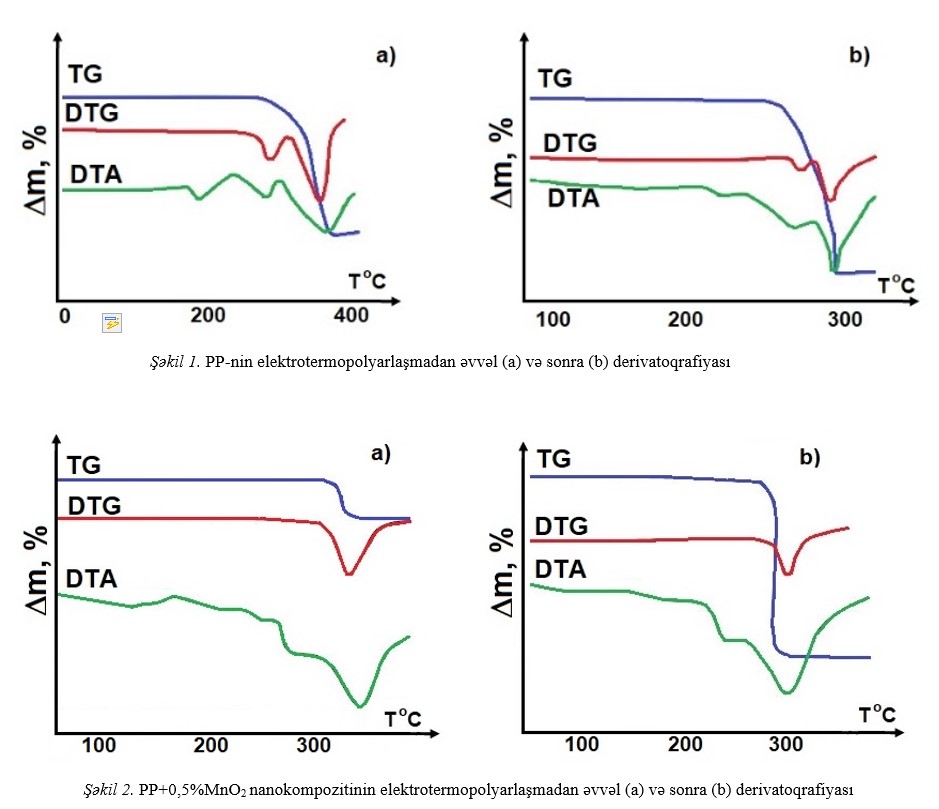
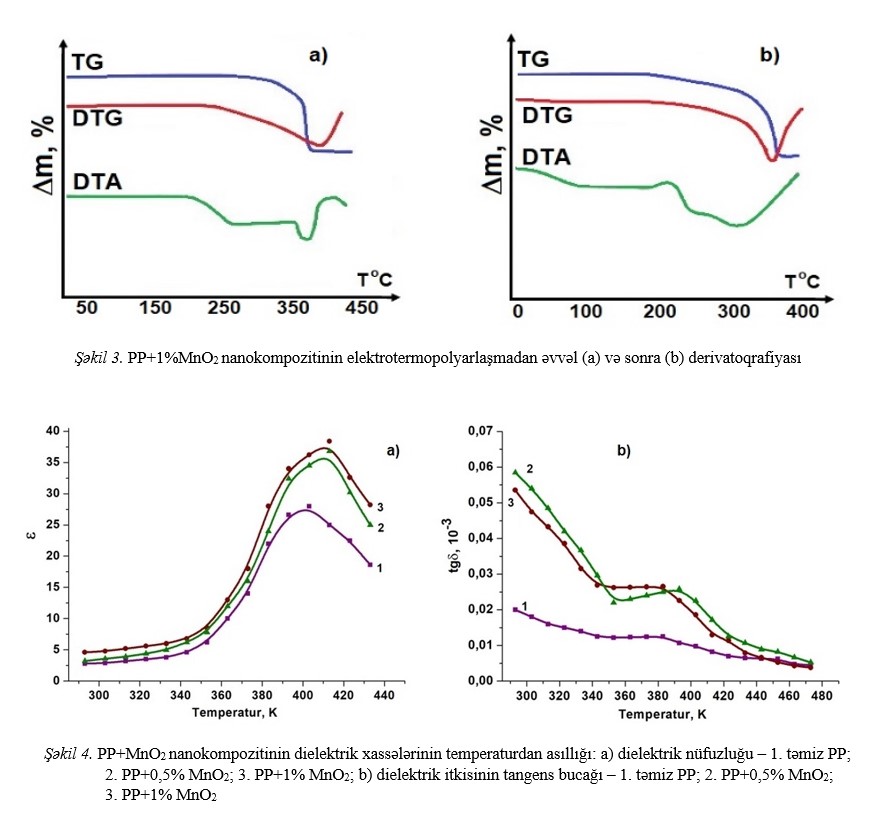
Fig.1-2 Fig.3-4
|
[1] A. Dutta, A.K. Ghosh. Investigation on γ-irradiated PP/ethylene acrylic elastomer TPVs by rheological and thermal approaches. Radiat. Phys. Chem., 144, 2018, 149-158.
[2] P. Dahal, Y.C. Kim. Preparation and characterization of modified polypropylene by using electron beam irradiation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 19, 2013, 1879-1883.
[3] M. Tulika, R. Bajpai. A thermally stimulated depolarization current investigation of poly (phenylene oxide): Poly(styrene) polymer blends. J. Physic, 2005, Vol.79, 4, 361-366.
[4] M. Gahleitner, K. Bernreitner, W. Neibl, C. Paulik, E. Ratajski. Influence of molecular structure on crystallization behaviour and mechanical properties of polypropylene. Polym. Test., 14, 1995, 173-187.
[5] I. Krupa, A.S. Luyt. Thermal properties of isotactic polypropylene degraded with gamma irradiation. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 72, 2001, 505-508.
[6] H.L. Sui, X.Y. Liu, F.C. Zhong, X.Y. Li, X. Ju. A study of radiation effects on polyester urethane using two-dimensional correlation analysis based on thermogravimetric data. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 98, 2013, 255-260.
[7] A. Fina, H.C.L. Abbenhuis, D. Tabuani, A. Frache G. Camino. Polypropylene metal functionalized POSS nanocomposites: a study by thermogravimetric analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 91, 2006, 1064-1070.
[8] А.Д. Стадник, Г.К. Кирик. Полимерные композиты и нанокомпозиты в магнитных полях, 2005, 239.
[9] A.B. Волков, M.A. Москвина, C.Б. Зезин. ВМС 1980. Сер. А, Т 45, 2, 2003, 283-291.
[10] B.A. Волков, M. Москвина, A. Волынский, Н.Ф. Бакеев. ВМС, Сер. А, Т 41, 6, 1999, 963-969.
[11] M.A. Ramazanov, A.M. Rahimli. The study of the morphology and dielectric properties of PVC/TiO2 based nanocomposites. An International Journal Integrated Ferroelectrics, Vol. 201, 1, 2019, 178-182.
[12] A. Nabiyev, A. Islamov, A. Maharramov, M. Nuriyev, R. Ismayilova, A. Doroshkevic, A. Pawlukojc, V. Turchenko, A. Olejniczak, M. Rulev, V. Almasan, A. Kuklin. Structural Studies of dielectric HDPE+ZrO2 polymer nanocomposites: filler concentration dependences, Physics: Conf. Series, United Kingdom, 994, 2018, 012011
[13] A. Magerramov, M. Ramazanov, F. Gadzhieva. Study of the Structure and Dielectric Properties of Nanocomposites Based on Polypropylene and Zirconia Nanoparticles, Surf. Eng. Appl. Chem.49, 2013, 355-358
[14] P. Patel, J. Rani, K. Yadav. Effective strategies for reduced dielectric loss in ceramic/ polymer nanocomposite film Ceram. Int, 47, 7, Part A, 2021, 10096-10103
[15] C. Zhang, R. Mason, G. Stevens. Dielectric Properties of Epoxy and Polyethylene, Nanocomposites Proceedings of 2005 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials, June 5-9, Kitakyushu, Japan, 2005, 393-396
|
