ABSTRACT
The optical properties of semiconductor superlattices are considered - solid-state structures in which, in addition to the periodic potential of the crystal lattice, there
is an additional one-dimensional potential, the period of which significantly exceeds the lattice constant.
Keywords: semiconductor superlattice, absorption coefficient, Wannier-Stark energy level, magnetophonon resonance.
DOI:10.70784/azip.1.2024309
Received: 10.07.2024
Internet publishing: 14.08.2024
AUTHORS & AFFILIATIONS
Institute of Physics Ministry of Science and Education Republic of Azerbaijan, 131 H.Javid ave, Baku, AZ-1143, Azerbaijan
E-mail: zalova0300@gmail.com
Graphics and Images
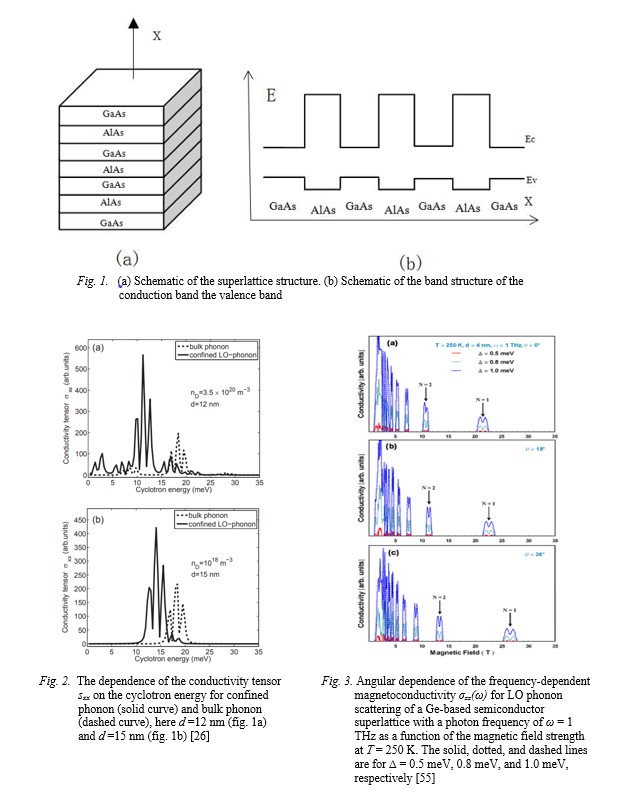
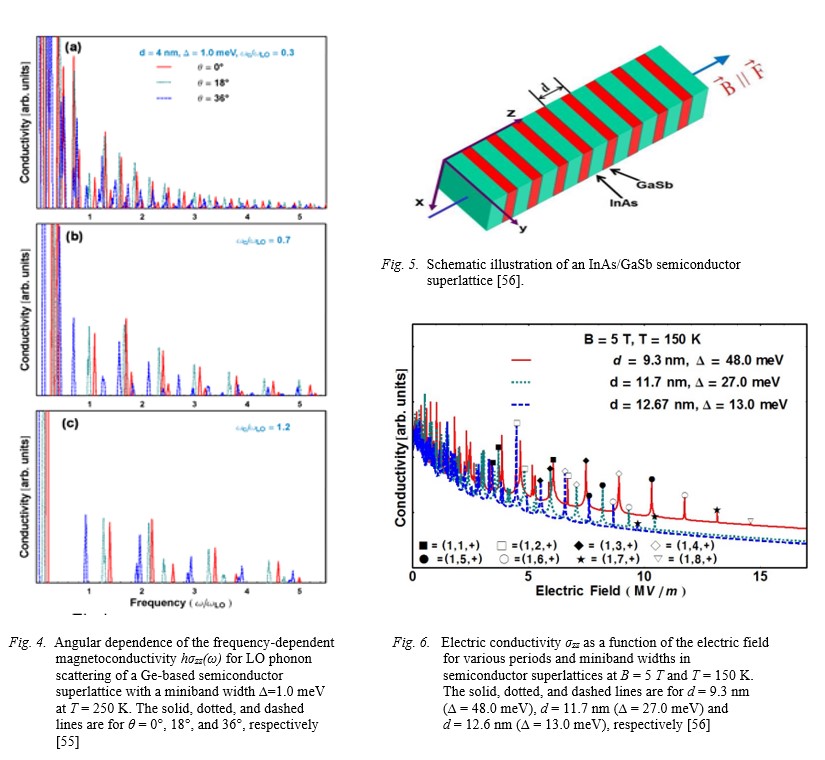
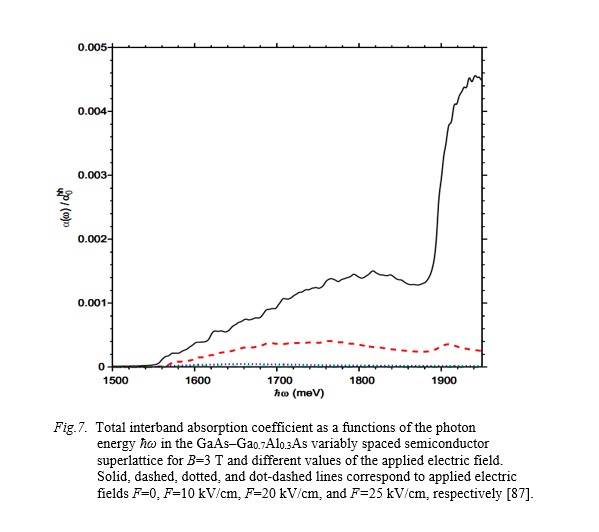
Fig.1-2-3 Fig.4-5-6 Fig.7
|
REFERENCIES
[1] A. Wacker. Semiconductor superlattices: a model system for nonlinear transport. Phys. Rep. 357, 1-111, 2002.
[2] A.Y. Shik. Sov. Current-voltage characteristic of a narrow-band semiconductor taking account into ionization impurities. Phys. Semicond. 8, 1195,1975.
[3] L. Esaki, R. Tsu. Superlattice and negative differential conductivity in semiconductors. IBM J. Res. Develop. 14, 61, 1970.
[4] A.Ya. Shik. Superlattices-periodic semiconductor structures. FTP,1974, t.8, № 10, s. 1841-1864
[5] E. Schomburg, J. Grenzer, K. Hofbeck, T. Blomeier, S. Winnerl, S. Brandl, A.A. Ignatov, K.F. Renk, D.G. Pavel’ev, Y. Koschurinov, V. Ustinov, A. Zhukov, A.Kovsch, S. Ivanov, P.S. Kop’ev. Ultrafast creation and annihilation of space-charge domains in a semiconductor superlattice observed by use of Terahertz fields. Solid-State Electronics 42 1495, 1998.
[6] Y. Shimada, K. Hirakawa, M. Odnoblioudov, and K. A. Chao. Terahertz Conductivity and Possible Bloch Gain in Semiconductor Superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 046806, 2003.
[7] P.G. Savvidis, B. Kolasa, G. Lee and S.J. Allen. Resonant Crossover of Terahertz Loss to the Gain of a Bloch Oscillating InAs/AlSb superlattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 196802, 2004.
[8] E. Schöll. Nonlinear spatio-temporal dynamics and chaos in semiconductors (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001). Nonlinear Science Series, Vol. 10.
[9] L.L. Bonilla and H.T. Grahn. Non-linear dynamics of semiconductor superlattices. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 577, 2005.
[10] Y. Zhang, J. Kastrup, R. Klann, K.H. Ploog and H.T. Grahn. Synchronization and Chaos Induced by Resonant Tunneling in GaAs/AlAs Superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3001,1996.
[11] K.N. Alekseev, G.P. Berman, D.K. Campbell, E.H. Cannon and M.C. Cargo. Dissipative chaos in semiconductor superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 54, 10625, 1996.
[12] A. Amann, J. Schlesner, A. Wacker and E. Schöll. Chaotic front dynamics in semiconductor superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 65, 193313, 2002.
[13] T.M. Fromhold, A.A. Krokhin, C.R.. Tench, S. Bujkiewicz, P.B. Wilkinson, F.W. Sheard and L.Eave. Effects of Stochastic Webs on Chaotic Electron Transport in Semiconductor Superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 046803, 2001.
[14] T.M. Fromhold, A. Patanè, S. Bujkievicz, P.B. Wilkinson, D.Powler, D. Sherwood, S.P. Stapleton, A.A. Krokhin, L. Eaves, M. Henini, N.S. Sankeshwar and F.W. Sheard. Chaotic electron diffusion through stochastic web enhances current flow in superlattices. Nature 428, 726, 2004.
[15] D.P.A. Hardwick, S.L. Naylor, S. Bujkiewicz, T.M. Fromhold, D. Fowler, A. Patanè, L. Eaves, A.A. Krokhin, P.B. Wilkinson, M. Henini and F.W. Sheard. Effect of interminiband tunneling on current resonances due to the formation of stochastic conduction networks in superlattices. Physica E 32, 285, 2006.
[16] Y.A. Kosevich, A.B. Hummel, H.G. Roskos, and K. Köhler. Ultrafast Fiske effect in semiconductor superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 137403, 2006.
[17] R.Z. Sagdeev, D.A. Usikov and G.M. Zaslavsky. Deterministic Chaos of Exponential Oscillons and Pulsons, Nonlinear Physics (Harwood Academic Publishers, NY, 1988).
[18] G.M. Zaslavsky, R.Z. Sagdeev, D.A. Usikov, A.A. Chernikov. Weak Chaos and Quasi-Regular Patterns. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991.
[19] A.A. Vasiliev, G.M. Zaslavsky, M.Y. Natenzon, A.I. Neishtadt, B.A. Petrovichev, R.Z. Sagdeev, A.A. Chernikov. Attractors and stochastic attractors of motion in a magnetic field. Sov. Phys. JETP 67, 2053, 1989. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 94, 170, 1988.
[20] S.P. Stapleton, S. Bujkiewicz, T.M. Fromhold, P.B. Wilkinson, A. Patan`e, L. Eaves, A.A. Krokhin, M. Henini, N.S. Sankeshwar and F.W. Sheard. Use of stochastic web patterns to control electron transport in semiconductor superlattices. Physica D 199, 166, 2004.
[21] A.G. Balanov, D. Fowler, A. Patan`e, L. Eaves and T.M. Fromhold. Bifurcations and chaos in semiconductor superlattices with a tilted magnetic field.
[22] V.L. Malevich and E.M. Epshtein. Photostimulated odd magnetoresistance of semiconductors. Sov. Phys. Solid State (Fiz. Tverd. Tela) 18, 1976, 1286.
[23] G.M. Shmelev, A.V. Yudina, I.I. Maglevanny and A.S. Bulygin. Electric-field-induced Ettingshausen in a superlattice. Phys. Stat. Sol.(b) 219, 2000, 115.
[24] Dao Thu Hang, Nguyen Vu Nhan and Nguyen Quang Bau. Theoretical Study of the Magneto-Thermoelectric Effect in Doped Semiconductor Superlattices under the Influence of an Electromagnetic Wave by Using a Quantum Kinetic Equation Key Engineering Materials. Vol. 783, pp 93-102.
[25] Dong Shik Kang, Suck, Whan Kim, Sang Chil Lee. Orbital Magnetization and Heat Capacity in Bulk Semiconductor Superlattices under a Tilted Magnetic Field. New Physics: Sae Mulli (The Korean Physical Society), vol. 61, № 5, 2011.
[26] Nguyen Quang Bau, Do Tuan Long. Impact of confined LO-phonons on the Hall effect in doped semiconductor superlattices Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices Volume 1, Issue 2, June 2016, Pages 209-213
[27] D.Z. Mowbray, M. Cardona, K. Ploog. Confined LO phonons in GaAs/AlAs superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 43, 1991, 1598e1603.
[28] J.S. Bhat, B.G. Mulimani, S.S. Kubakaddi. Electron-confined LO phonon scattering rates in GaAs/AlAs quantum wells in the presence of a quantizing magnetic field. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 8, 1993, 1571e1574.
[29] N.Q. Bau, D.M. Hung, L.T. Hung. The influences of confined phonons on the nonlinear absorption coefficient of a strong electromagnetic wave by confined electrons in doping superlattices. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 15, 2010, 175e185.
[30] A.M. Paula, G. Weber. Carrier capture processes in semiconductor superlattices due to emission of confined phonons. J. Appl. Phys. 77, 1995, 6306e6312.
[31] A. Fasolino, E. Molinari, J.C. Maan. Resonant quasiconfined optical phonons in semiconductor superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 39, 1989, 3923e3926.
[32] P.Y. Yu, M. Cardona. Fundamentals of Semiconductors. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005, pp. 469e551.
[33] S. Rudin, T. Reinecke. Electron-LO-phonon scattering rates in semiconductor quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 41, 1990, 7713e7717.
[34] N.Q. Bau, B.D. Hoi. Dependence of the Hall coefficient on doping concentration in doped semiconductor superlattices with a perpendicular magnetic field. Integrated Ferroelectrics Số 1, năm 2014 (Tập 155, trang 39-44)
[35] Sang Chil Lee and Dong Shik Kang, Jeong Dae Ko, Young Hun Yu and Jai Yon Ryu, Suck Whan Kim. Magnetophonon Resonances in the Miniband Transport in Semiconductor Superlattices. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 39, No. 4, October 2001, pp. 643- 654.
[36] M.A. Brummell, D.R. Leadley, R.J. Nicholas, M.A. Hopkins, J.J. Harris and C.T. Foxon. Modification of the Electron-Phonon Interactions in GaAs-GaAlAs Heterojunctions.Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 77, 1988.
[37] W. Xu, F.M. Peeters, J.T. Devreese, D. R. Leadley and R. J. Nicholas, Int. J. Mod. Destruction of magnetophonon resonance in high magnetic fields from impurity and phonon scattering in heterojunctions. Phys. B 10, 169, 1996.
[38] S.C. Lee, J.Y. Ryu, S.W. Kim and C. S. Ting. Magnetization and magnetic susceptibility in a quantum-dot superlattice at low temperature. Phys. Rev. B 62, 5045, 2000.
[39] H. Noguchi, H. Sakaki, T. Takamasu and N.Miura. Observation of magnetophonon resonance in the miniband transport in semiconductor superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 45, 12148 (1992).
[40] W.M. Shu and X.L. Lei. Miniband transport in semiconductor superlattices in a quantized magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 50, 17378, 1994.
[41] P. Gassot, J. Genoe, D. K. Maude, J.C. Portal, K. S.H. Dalton, D.M. Symons, R.J. Nicholas, F. Aristone, J.F. Palmier and F. Laruelle. Magnetophonons in short-period superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 54, 14540, 1996.
[42] V.L. Gurevich, Yu.A. Firsov. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 40, 1961, 198, Sov. Phys. JETP 13, 1961, 137.
[43] P. Vasilopoulos. Magnetophonon oscillations in quasi-two-dimensional quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 33, 1986, 8587.
[44] N. Mori, K. Taniguchi, C. Hamaguchi, S. Sasa, S. Hiyamizu. Magnetophonon resonance of a two dimensional electron gas in a quantum well. J. Phys. C 21, 1988, 1791.
[45] A. Suzuki. Theory of hot-electron magnetophonon resonance in quasi-two-dimensional quantum-well structures. Phys. Rev. B 45, 1992, 6731.
[46] P. Vasilopoulos, P. Warmenbol, F.M. Peeters, J.T. Devreese. Magnetophonon resonances in quasi-one-dimensional wires. Phys.Rev. B 40, 1989, 1810.
[47] N. Mori, H. Momose, C. Hamaguchi. Magnetophonon resonances in quantum wires. Phys. Rev. B 45, 1992, 4536.
[48] J.Y. Ryu, R.F. O’Connell. Magnetophonon resonances in quasi-one-dimensional quantum wires. Phys. Rev. B 48, 1993, 9126.
[49] J.Y. Ryu, G.Y. Hu, R.F. O’Connell. Magnetophonon resonances of quantum wires in tilted magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. 49, 1994, 10437.
[50] J.P. Vasilopoulos, M. Charbonneau, C.M. Van Vliet. Linear and nonlinear electrical conduction in quasi-two-dimensional quantum wells, Phys. Rev. B 35, 1987, 1334.
[51] A. Suzuki, M. Ogawa. Magnetophonon resonance of quasi-two-dimensional and quasi-one-dimensional electronic systems in tilted magnetic fields. J. Phys. C 10, 1998, 4659.
[52] H. Noguchi, H. Sakaki, T. Takamasu, N. Miura. Observation of magnetophonon resonance in the miniband transport in semiconductor superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 45 (1992) 12148.
[53] W.M. Shu, X.L. Lei. Miniband transport in semiconductor superlattices in a quantized magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 50, 1994, 17378.
[54] X.L. Lei, N.J.M. Horing, H.L. Cui. Theory of negative differential conductivity in a superlattice miniband. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 1991, 3277.
[55] Sang Chil Leea, Jeong Woo Kanga, Dong Shik Kanga, Young Bong Kanga, Kyung Hwa Kimb,Hyung Soo Ahnb, Min Yangb, Nam Lyong Kangc, Suck Whan Kimd. Angular dependence of magnetophonon resonances in semiconductor superlattices in tilted magnetic fields. Physica B 387, 2007, 313–322.
[56] Sang Chil Lee, Hyung Soo Ahn, Suck Whan Kim. Wannier-Stark Mangnetophonon Resonance in Semiconductor Superlattices New Physics: Sae Mulli, Vol. 66, № 11, November 2016, pp. 1359∼1365
[57] Nguyen Hong Shon and H.N. Nazareno. Hopping conduction in semiconductor superlattices in a quantized magnetic field.Physical Review b, volume 53, number 12, 1996.
[58] A.Ya. Shik. Fiz. Tekh. Poluprovodn. 7, 261, 1973. [Sov. Phys. Semicond. 7, 187 1973)].
[59] R.A. Suris and B.S. Shchamkhalova. Heating of electrons in superlattice semiconductors. Fiz. Tekh. Poluprovodn. 18, 1178, 1984, [Sov. Phys. Semicond. 18, 738, 1984].
[60] Kazarinov and R.A. Suris. Electric and electromagnetic properties of semiconductors with a superlattice, Fiz. Tekh. Poluprovodn. 6, 148, 1972, Sov. Phys. Semicond. 6, 120,1972.
[61] Nguyen Hong Shon and H.N. Nazareno. Influence of quantum-interference effects on hole mobility in superlattices, Rev. B 50, 8577 1994.
[62] S.R. Eric Yang and S. Das Sarma. Theory of conductivity in superlattice minibands. Phys. Rev. B 37, 10 090, 1988.
[63] R. Tsu and G. Do ̈hler. Phys. Rev. B 12, 680, 1975; G.H. Döhler, R. Tsu, and L. Esaki. Solid State Commun. 17, 317, 1975.
[64] R. Tsu and L. Esaki. Phys. Rev. B 43, 5204 1991.
[65] Jian-Bai Xia. Phys. Rev. B 50, 15 067, 1994.
[66] C.J. Summers, K.F. Brennan. Variably spaced superlattice energy filter, a new device design concept for high-energy electron injection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 48 (12), 1986, 806–808.
[67] K.F. Brennan, C.J. Summers. Theory of resonant tunneling in a variably spaced multiquantum well structure: an Airy function approach. J. Appl. Phys. 61 (2), 1987, 614–623.
[68] K.F. Brennan, C.J. Summers. The variably spaced superlattice electroluminescent display: a new high efficiency electroluminescence scheme. J. Appl. Phys. 61 (12), 1987, 5410–5418.
[69] C.J. Summers, K.F. Brennan. New resonant tunneling superlattice avalanche photodiode device structure for long-wavelength infrared detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 51 (4), 1987, 276–278.
[70] S.M. Cao, M. Willander, E.L. Ivchenko, A.I. Nesvizhskii, A.A. Toropov. Electrons and excitons in an imperfect superlattice in electric fields. Superlatt. Micro-struct. 17 (1), 1995, 97–105.
[71] S.M. Cao, M. Willander, A.A. Toropov, T.V. Shubina, B.Y. Mel'tser, S.V. Shaposhnikov, P.S. Kop'ev, P.O. Holtz, J.P. Bergman, B. Monemar. Resonant coupling of electrons and excitons in an aperiodic superlattice under electric fields studied by photoluminescence spectroscop. Phys. Rev. B 51, 1995, 17267–17270.
[72] S.M. Cao, M. Willander, A.A. Toropov, T.V. Shubina, B.Y. Mel'tser, S. V. Shaposhnikov, P.S. Kop'ev, J.P. Bergman, P.O. Holtz, B. Monemar. Characterization of Al0.4Ga0.6As/GaAs aperiodic superlattices by photoluminescence spectroscopy at 2 K. Superlatt. Microstruct. 20 (2), 1996, 229–235.
[73] S.M. Cao, M. Willander, A.A. Toropov, T.V. Shubina, B.Y. Mel'tser, P.S. Kop'ev, T. Lundström, P.O. Holtz, J.P. Bergman, B. Monemar. Bistable electroluminescence in p-i-n light-emitting tunnel-diodes enhanced by aperiodic-superlattice injectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72 (3), 1998, 347–349.
[74] K.W.J. Barnham, G. Duggan. A new approach to high efficiency multiband gap solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 67 (7), 1990, 3490–3493.
[75] M. Courel, J.C. Rimada, L. Hernánde. GaAs/GaInNAs quantum well and superlattice solar cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 (7), 2012, 073508.
[76] M. Courel, J.C. Rimada, L. Hernández. An approach to high efficiencies using GaAs/GaInNAs multiple quantum well and superlattice solar cell. J. Appl. Phys. 112 (5), 2012, 054511.
[77] C.I. Cabrera, J.C. Rimada, M. Courel, L. Hernandez, J.P. Connolly, A. Enciso, D. A. Contreras-Solorio. Modeling multiple quantum well and superlattice solar cells. Nat. Resour. 04 (03), 2013, 235–245.
[78] C.I. Cabrera, J.C. Rimada, J.P. Connolly, L. Hernandez. Modeling of GaAsP/In-GaAs/GaAs strain-balanced multiple-quantum well solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 113 (2), 2013, 024512.
[79] B. Royall, H. Khalil, S. Mazzucato, A. Erol, N. Balkan. Experimental investigation and numerical modeling of photocurrent oscillations in lattice matched Ga1xInxNyAs1y/GaAs quantum well p-i-n photodiodes. Nanosc. Res. Lett. 9 (1), 2014, 84.
[80] M.L. Leadbeater, L. Eaves, P.E. Simmonds, G.A. Toombs, F.W. Sheard, P.A. Claxton, G.Hill, M.A. Pate. Magnetic-field studies of negative differential conductivity in double barrier resonant tunnelling structures based on n InP/ (InGa)As, Solid-State Electron. 31 (3–4), 1988, 707–710.
[81] H.J. Hutchinson, A.W. Higgs, D.C. Herbert, G.W. Smith. Observation of miniband transport in GaAs/Al0.33Ga0.67As superlattices. J. Appl. Phys. 75 (1), 1994, 320–324.
[82] W.M. Shu, X.L. Lei. Miniband transport in semiconductor superlattices in a quantized magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 50 (23), 1994, 17378–17382.
[83] S. Blaser, L. Diehl, M. Beck, J. Faist. Long-wavelength (λ∼10.5 μm) quantum cascade lasers based on a photon-assisted tunneling transition in strong magnetic field. Physica E 7 (1–2), 2000, 33–36.
[84] G.G. Zegrya, N.V. Tkach, I.V. Boiko, Y.A. Seti. Quasi-stationary electron states in a multilayered structure in longitudinal electric and transverse magnetic fields. Phys. Solid State 55 (10), 2013, 2182–2189.
[85] J. Silvano de Sousa, H. Detz, P. Klang, E.Gornik, G. Strasser, J. Smoliner. Enhanced Rashba effect in transverse magnetic fields observed on InGaAs/ GaAsSb resonant tunneling diodes at temperatures up to T1⁄4180 K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 (15), 2011, 152107.
[86] E. Reyes-Gómez, N. Raigoza, L.E. Oliveira. Intraband absorption in GaAs–(Ga,Al)As variably spaced semiconductor superlattices under crossed electric and magnetic fields Europhys. Lett. 104 (4), 2013, 47008.
[87] J.N. Zuleta, E. Reyes-Gómez. Effects of crossed electric and magnetic fields on the interband optical absorption spectra of variably spaced semiconductor superlattices. Physica B: Condensed Matter Volume 488, 1 May 2016, Pages 72-82.
[88] G.B. Ibragimova and R.Z. Ibaevaa. Light Absorption by Free Charge Carriers with Scattering Mechanisms in a Semiconductor Superlattice. Journal of Surface Investigation: X-ray, Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques, 2024, Vol. 18, № 1, pp. 116–120.
[89] M. Jiang, H. Y. Xiao, S. M. Peng, L. Qiao, G. X. Yang, Z. J. Liu, and X. T. Zu. Effects of stacking periodicity on the electronic and optical properties of GaAs/AlAs superlattice: a first-principles study. Sci. Rep. 10, 4862, 2020.
[90] S. Hubmann, V. V. Belkov, L. E. Golub, V. Yu. Kacho-rovskii, M. Drienovsky, J. Eroms, D. Weiss, and S. D. Ganichev. Giant ratchet magneto-photocurrent in graphene lateral superlattices. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 033186 (2020).
[91] H. Ghulam, C. Giuseppe, I. Rajibul, T. Artur, J. Jarosław, A. Carmine, and D. Tomasz. J. Phys. D. 55,495301, 2022.
|
